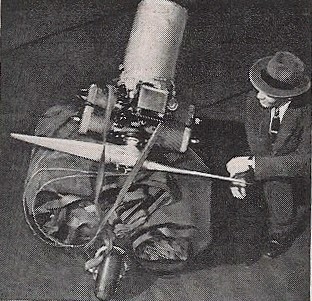
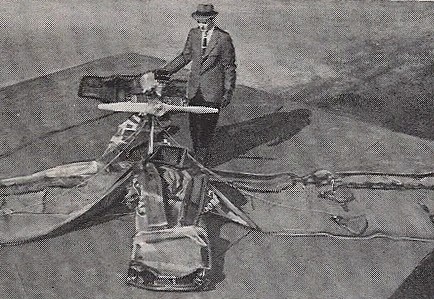

Inflatoplanes!



The UAV fad has spurred another look at inflatable airplanes to get aircraft capabilities through structures that minimize themselves when not in use:
www.combatreform.com/AIAA2003_6630.pdf
The essential problem in flight by air pressure differential is that you need lots of wing or some kind of surface area to create lift that on the ground gets in the way of moving the aircraft around. An airplane that deflates would be an extreme form of wing folding--the entire aircraft can be deflated until use.
Imagine an inflatoplane made of CLEAR see-through material that would blend into the sky. Engine would be a silenced diesel engine of about 75 horsepower. Soldier pilot/observer would wear sky gray colored nomex jumpsuits and helmets to assist in blending in with the sky.
Inflatoplane would be inflated with non-flammable HELIUM to shed about 20 pounds of weight to increase range.

Its standard practice throughout the world to use inflatable boats...if the military mind can accept his life depending on a Zodiac F470 boat in the water, why not an inflatable airplane? And an excellent place to start for a military inflatable SEAPLANE would be with the Navy SEALS deploying from nuclear submarines covertly.
http://72.14.209.104/search?q=cache:ft7cqQuG8PoJ:encyclopedia.quickseek.com/index.php/Goodyear_Inflatoplane+ga-466+inflatoplane&hl=en&gl=us&ct=clnk&cd=1
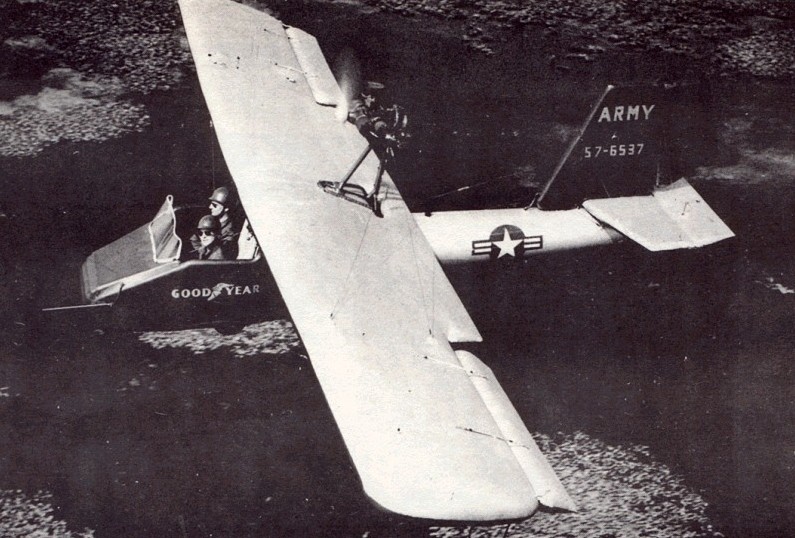
Goodyear Inflatoplane
From QuickSeek Encyclopedia
The Goodyear Inflatoplane was an experimental aircraft made by the Goodyear Aircraft Company, a subsidiary of Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company, well known for the Goodyear blimp. The Inflatoplane was roughly equivalent to the Piper Cub.
The all-fabric inflatable aircraft was built in 1956, with the idea that it could be used by the military as a rescue plane to be dropped in a box behind enemy lines. Only 12 were built, but development continued until the project was cancelled in 1973.
There were at least 2 versions:

The GA-468 was a single seater. It took about 5 minutes to inflate to about 25 lbf/in² (170 kPa); at full size it was 19 ft 7 in (5.97 m) long, with a 22 ft (6.7 m) wingspan. A pilot would then hand start the two-stroke cycle, 40 hp (30 kW) engine, and take off with a maximum load of 240 lb (109 kg). On 20 US gallons (76 L) of fuel, the aircraft could fly 390 miles (630 km), with an endurance of 6.5 hours. Maximum speed was 72 mph (116 km/h). Later, a 42 hp (31 kW) engine was used in the plane.
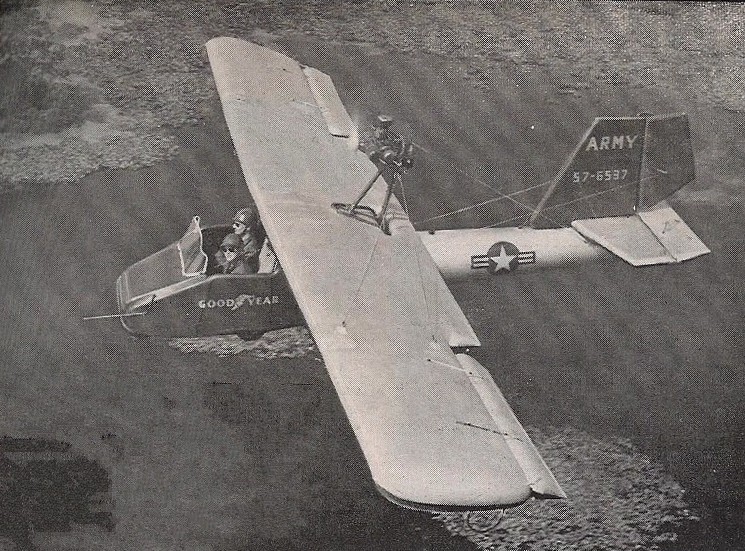

The GA-466 was the two seater version, 2 in (50 mm) shorter, but with a 6 ft (1.8 m) longer wingspan than the GA-468. A more powerful 60 hp (45 kW) McCulloch 4318 engine could power the 740 lb (336 kg) of plane and passenger to 70 mph (113 km/h), although the range of the plane was limited to 275 miles (440 km).
THE GOODYEAR MODEL 466 & 468 INFLATOPLANE
The Goodyear Inflatoplane is a light aircraft with a completely pneumatic airframe. The wing and tail assemblies are made of a rubberised fabric developed by Goodyear and called Airmat, which consists of two layers of nylon fabric joined by thousands of dropped threads. When inflated the layers of nylon are forced apart, the threads being stretched taut to maintain the correct surface contours. The fuselage is of simple rubberised airship fabric. The entire aircraft when deflated can be transported in a truck, jeep, trailer or aircraft (for air-dropping). It can be inflated from a compressed air bottle or by manual pump. Maximum inflation pressure is 7 lb./ sq. in. (0.49 kg. cm.²) for the single-seat version, and 8.5 Ib./sq. in. (0.60 kg./ cm.²) for the two-seat model.
The Inflatoplane has a horizontally-opposed air-cooled two-stroke engine, mounted above the rear of the wing and driving a two-blade wooden tractor air-screw.
Flying controls ere conventional and the rigidity of the wing is such that it will support the weight of a man on each side immediately outboard of the bracing struts.

Since the original prototype flew in 1956, several improved versions have been developed under military contracts, with both open and enclosed cockpits and alternative wheel and single hydroski landing gear to land on water and snow.
On those models, a compressor can be fitted at the back of the engine to maintain pressure in the airframe even when a number of .30 in. caliber bullets have pierced the fabric.
The two current versions of the Inflatoplane are :-
Model 466 (XAO-2G1). Two-seater with 63 h.p. McCulloch 4318E engine.

-------------------------------------------------
DIMENSIONS (Model GA-466).- Span 28 ft. (8.5 m.) Length 19 ft. 8 in. (8.0 m.)
WEIGHTS (Model GA.466).- Weight empty 290 Ib. (130 kg.) Weight loaded 740 Ib. (336 kg.)
PERFORMANCE (Model GA-466). Max. speed 70 m.p.h. (112 km.h.) Cruising speed 55 m.p.h. (88 km.h.) Stalling speed 43 m.p.h. (69 km.h.) Rate of climb at S/L 500 ft./min. (152 m./min.) Service ceiling 6,500 ft. (1,980 m.) Take-off run (grass) 390 ft. (120 ft.) Endurance 5.4 hours.
GA-466
Wings
28 feet length x 6 feet wide x 1 feet high = 168 cubic feet of helium
Fuselage
20 feet length x 3 feet wide x 2 feet high = 120 cubic feet of helium
______________________________________________________
388 cubic feet of helium =
One cubic foot of helium will lift about 28.2 grams = 10, 941.6 grams =
22.42 pounds of buoyant lift
Empty weight 290.00 pounds
Helium lift 22.42 pounds
_________________________
267.58
Model 468 (XAO-3G1). Single-seater, with 44 h.p. Nelson H-63A engine. Five built for U.S. Navy, five for U.S. Army.

DIMENSIONS (Model GA-468).- Span 22 ft. (6.7 m.) Length 19 ft. 8 in. (8.0 m.)
WEIGHTS (Model GA-468).-Weight empty 225 Ib. (102 kg.) Weight loaded 550 Ib. (250 kg.)
PERFORMANCE (Model GA-468).- Max. speed 72 m.p.h. (115 km.h.) Cruising speed 60 m.p.h. (96 km.h.) Stalling speed 37 m.p.h. (59 km.h.) Rate of climb at S/L 550 ft./min. (170 m./min.) Service ceiling 10,300 ft. (3,140 m.) Take-off run (grass) 250 ft. (76 m.) Landing run (grass) 350 ft. (107 m.) Endurance 6.5 hours
GA-468
Wings
22 feet length x 6 feet wide x 1 feet high = 132 cubic feet of helium
Fuselage
20 feet length x 3 feet wide x 2 feet high = 120 cubic feet of helium
______________________________________________________
252 cubic feet of helium =
One cubic foot of helium will lift about 28.2 grams = 7, 106.4 grams =
14.56 pounds of buoyant lift
Empty weight 225.00 pounds
Helium lift 14.56 pounds
_________________________
210.44 pounds
NOTES
http://science.howstuffworks.com/helium2.htm
One cubic foot of helium will lift about 28.2 grams
Multiply the volume of the balloon by 28.2. Divide by 448 -- the number of grams in a pound -- to determine the number of pounds it can lift.